Engineering Technologies
FOTEC operates a modern and state-of-the-art laboratory for additive manufacturing (3D printing) of metals and polymers.
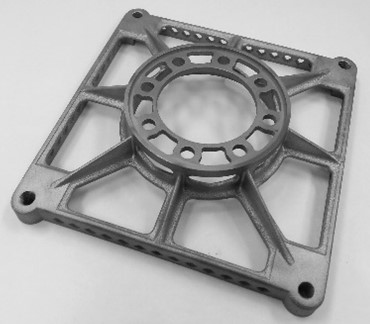
Since 2010 highly complex prototypes and structural parts are designed and manufactured at FOTEC using the laser beam melting (LBM) technology. Additive manufacturing offers a high degree of design freedom, which cannot be yielded with conventional technologies such as milling.
Furthermore, FOTEC operates a laboratory for powder injection molding (PIM) of metallic (MIM) and ceramic (CIM) parts.
Click here for our brochure (only available in German)

ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING (3D PRINTING)
Additive manufacturing opens up new possibilities in component development and prototype production. FOTEC operates a modern laboratory for 3D printing of metals and polymers and would be happy to support you in this field as an experienced and competent development and research partner.
ANALYTICS/MEASUREMENT TECHNOLOGIES
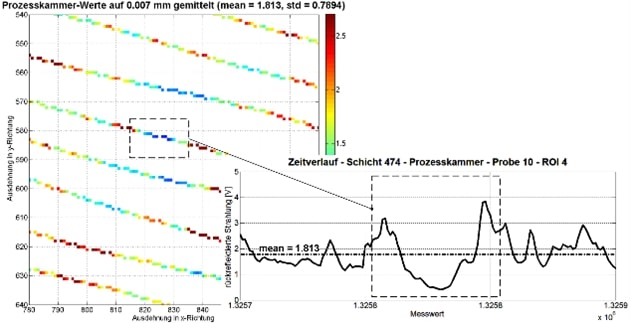
Powder analysis, tactile and optical 3D measurement of parts can be performed at FOTEC. Surface properties of parts can be characterized via optical focus variation.
ENGINEERING
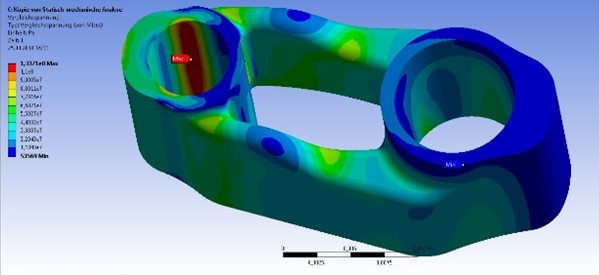
Our team of mechatronics, mechanical and electrical engineers would be happy to assist you with CAD design, finite element (FE) analysis or with designing and building complex mechatronic systems.

CONSULTING & EDUCATION
Do you need consulting or training in the fields of manufacturing technology in general and 3D printing processes such as LBM, FFF, SLA or SLS in particular? Contact us!
PROJECT UMCAWE
The goal of project UMCAWE is the electrochemical conversion of carbon dioxide (CO2) contained in exhaust gases from two different sources, cement production and biogas production, into methane gas. This gas can be used on-site in both industrial sectors (e.g. as fuel). The R&D work focuses on the following topics:
- Selection/development of suitable catalysts for the conversion of CO2 into methane
- Investigation of the effect of other components in the two different CO2-containing exhaust gases (cement and biogas) on the performance of the process
- Planning and construction of a test setup for the process
- Development of computer simulation models for the investigated electrochemical processes to further develop the catalysts
- Development of sensors to monitor the process in the aspired test setup
The findings can be used by Austrian industrial partners to increase the sustainability of their plants.


PROJECT AKTIVMAT
The goal of project AktivMAT is to develop new active materials (electrodes) for hydrogen production by splitting water using electrical current (= electrolysis). It focuses on the following topics:
- Development of 3D-printed porous electrodes for hydrogen production using alkaline electrolysis (AEL) based on stainless steel, nickel, and nickel alloys
- Development of surface treatments (e.g. etching processes, coatings) for 3D-printed and conventionally manufactured electrodes to improve their performance
- Development of a test setup to assess the performance and stability of the developed materials
- Evaluation of the technical and economic suitability of the developed materials and the corresponding electrolysis technology for implementation in the Austrian power grid (= techno-economic evaluation)
QUESTION(S)?
GET IN CONTACT WITH US
Dr. Markus Hatzenbichler
Head of the Engineering Technologies Department
Tel.: +43 5 0421 8202
E-Mail: hatzenbichler@fotec.at